Odds Versus Risk

Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
Q Tbn 3aand9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau
Confidence Intervals For Measures Of Effect Optional

Usa Risk Of Dying Of Covid 19 Versus Other Causes Poc

Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World

Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
The risk ratio, the incidence rate ratio, and the odds ratio are relative measures of effect.

Odds versus risk. The question of which statistic to use is subtle but very important. Important points about Odds ratio:. 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (3.00 in those who are non-obese versus 1.29 in those who are obese).
It can help us respond to danger more quickly or avoid a dangerous situation altogether. ‘odds in favor’ and ‘odds against’. Hazard ratio deals with a two part ( level ) explanatory variable and is an instantaneous risk over the course of the study.
The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical. The simple relative risk is 0.55 and the simple odds ratio is 0.25.Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis). It may confuse since both ‘Odds’ and ‘probability’ are related to the potential that event occurs.
The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples. (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio). It is the risk of a.
Both are calculated from simple 2x2 tables. Relative Risk and Odds Ratio Calculator This Relative Risk and Odds Ratio calculator allows you to determine the comparative risk of the occurrence of a significant event (or outcome) for two groups. Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probability.
Let’s look at an example. One example of this is odds and odds ratio. Published on December 14, 15 by Howard Herrell, MD.
The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and odds. Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program. Probability to Odds.
Thus in situations with rare outcomes an odds ratio can be interpreted as if it were a risk ratio, since they will be numerically similar. The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it’s that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities. A RR of 0.5 means the risk is cut in half.
A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold. In biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome. What is the probability that A will lose two points in a "2 on 2" attack using standard dice in the game of RISK?.
Therefore, odds ratios are generally interpreted as if they were risk ratios. Increasingly, they are also used to report the findings from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. We can’t do that in case control studies.
The relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology. Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (<10%). Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk.
Odds can have any value from zero to infinity and they represent a ratio of desired outcomes versus the field. A large battle is 3 or more attackers and 2 or more defenders. Comparing OR and Risk Ratio - OR Farther from 1.
The probability of it occurring is low), the odds and risk ratios are numerically quite similar. The net attrition rate, defined as the expected value of the difference between defender and attacker losses. No difference in risk log OR < 0:.
"The odds ratio is very similar to the risk ratio, particularly if a disease is rare. Without a doubt, clindamycin carries the highest risk of C difficile infection with an odds ratio of about 17- compared to no antibiotic exposure. Difference Between Odds Ratio and Relative Risk 1.
Odds ratios are a common measure of the size of an effect and may be reported in case-control studies, cohort studies, or clinical trials. Many great things have been written about the difference between Odds Ratios (OR) and Relative Risks (RR). Unfortunately, there is a recognised problem.
Until now we have learned the following:. Risk difference is an absolute measure of effect and it is calculated by subtracting the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals from that of unexposed. Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk.
Probability can be carefully defined using set theory and a few axioms, but the basic idea is that probability uses a real number between zero and one to measure the likelihood of an event occurring. Obviously, these results run counter. The odds for favorites will have a minus (-) sign, and represent the money you need to risk to win $100.
Odds ratio versus odds Author William Gould, StataCorp James Hardin, StataCorp Unfortunately, the language used to describe statistical terms is not used uniformly across fields. Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese:. $1 – the amount you wagered).
The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative risk. 2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the non-obese:. Your odds of dying from an accidental opioid overdose continue to be greater than dying in a motor-vehicle crash.
The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1.125, while the odds ratio is about 2.25. Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio. Factional, decimal, and.
That is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio. Decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio-4 -2 0 2 4. This is the "game of RISK" in which there is an "a on d" attack.
Therefore, the odds of rolling four on a dice are 1/5 or %. The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise. Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research.
For example, suppose the members of one group each eat a kilo of cheese every day, and the members of another group eat no cheese, and you have. Odds ratio versus relative risk. However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be used.
For large battles the army count has nothing to do with the outcome of any single battle, which means you only need to remember a single number:. A fractional listing of 6/1 (six-to-one) odds would mean that you win $6 against every $1 you wager (in addition to receiving your dollar back, i.e. The math underlying odds and gambling can help determine whether a wager is worth pursuing.
Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR). Essoe-Odds1 Back to the Superbowl example, the relative odds of being hungover today, associated with being a Seahawks fan would be Essoe-Odds2. Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret.
The first thing to understand is that there are three distinct types of odds:. Relative risk, Risk difference and Odds ratio. The RR is much simpler to interpret and is most likely consistent with everyone’s intuition.
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk. ‘Odds in favor’ are odds describing the if an event will occur, while ‘odds against’ will describe if an event will not occur. In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we.
There are a variety of ways to think about how to compute this number. The schematic below illustrates the point that, unless both the risk ratio and the odds ratio are 1.0 (no difference), The odds ratio is always farther from 1.0 than the risk ratio Larger if the risk ratio is greater than 1.0 and smaller if the risk ratio is less than 1.0. Absolute risk, attributable risk, attributable risk percent, population attributable risk percent, relative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others.
Probability vs Odds. "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables. Others use odds ratios (ORs).
The odds ratio can be used in observational studies (examining the effect of a risk factor/symptom on the disease outcome), prospective studies (where subjects who are initially identified as “disease-free” and classified by presence or absence of a risk factor are followed over time to see if they develop the disease) and retrospective studies (subjects are followed back in time to check for the presence or absence of the risk factor for each individual). In finer terms, odds is described as the probability that a certain event will happen or not. With an odds ratio, the outcome can be the starting point with which we can determine the relative odds of someone having been exposed to a risk factor.
Fear is natural and healthy. Odds ratio, risk ratio, and prevalence ratio are some of the measures of association which are often reported in research studies quantifying the relationship between an independent variable and the outcome of interest. However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association.
In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures. Every medical student at some point has been taught the difference. Economists especially refer to what others call the odds as the odds ratio.
The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk. The compared dice are discarded, and if both A and D still have dice left, we repeat the compare process above. OR is a bit more complicated and uses the formula A/ (1-A)/ B/ (1-B).
Some studies use relative risks (RRs) to describe results;. It can also cause us to worry about the wrong things, especially when it comes to estimating our level of risk. We can calculate relative risk IF we can estimate probabilities of an outcome in EACH group.
One way is to think about performing an experiment several times. We are 95% confident that the true odds ratio is between 1.85 and 23.94. Odds ratios are hard to comprehend directly and are usually interpreted as being equivalent to the relative risk.
Real life is full of incidents with uncertainty. While odds for an event indicates the probability that the event will occur, whereas odds against will reflect the likelihood of non-occurrence of the event. For the odds ratio to be a good approximation, the cases and controls must be representative of the general.
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure. In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the.
These are all part of Survival Analysis a statistical method used in clinical trials. Alternatively, we can also use it to describe the ratio of disease odds given the exposure status. The log OR comparing women to men is log(1.44) = 0.36 The log OR comparing men to women is log(0.69) = -0.36 log OR > 0:.
When the data to be analyzed consist of counts in a cross-classification of two groups (or conditions) and two outcomes, the data can be represented in a fourfold table as follows:. Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarized. The null value is 1, and because this confidence interval does not include 1, the result indicates a statistically significant difference in the odds of breast cancer women with versus low DDT exposure.
3-5 Fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, aztreonam, and carbapenems carry a fairly high risk, all of which being associated with an odds ratio of approximately 5 compared to no antibiotic exposure. The rationale for these guidelines is outlined below. In a study on men given a new stati.
Rather the odds is threefold greater. The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful. Yet these statistical terms are confused and.
That being said, if the odds of dying from all possible causes are 1 in 1, here are the lifetime odds of death for selected causes, from most likely to least:. Odds Ratio (OR) is a measure of association between exposure and an outcome. Odds of dying are affected by an individual’s activities, occupation, and where he or she lives and drives, among other things.
Odds are a ratio, and can be given in two different ways:. When the event of interest is rare (i.e. We see that the ‘relative risk’ is now different, but the odds ratio does not change if we change the ratio of cases versus controls.
The direct computation of relative risks is feasible if meaningful prevalences. There has been much debate on the issue of which measure is appropriate to repor …. Another attractive feature is that the odds ratio can be calculated with data from a case-control study, whereas neither a risk ratio nor a rate ratio can be calculated.
But an OR of 3 doesn’t mean the risk is threefold;. The terms probability and odds measure one’s belief in the occurrence of a future event. If they win, you profit $100 and get your original $140 back.
You need to risk $140 to win $100 on the Packers. Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome. Increased risk log OR = 0:.
However, there is a difference. The control group was 8.4 years older on average (43.5 years versus 35.1), showing the need to adjust for this variable. Probability is the likelihood of an event in relation to all possible events.
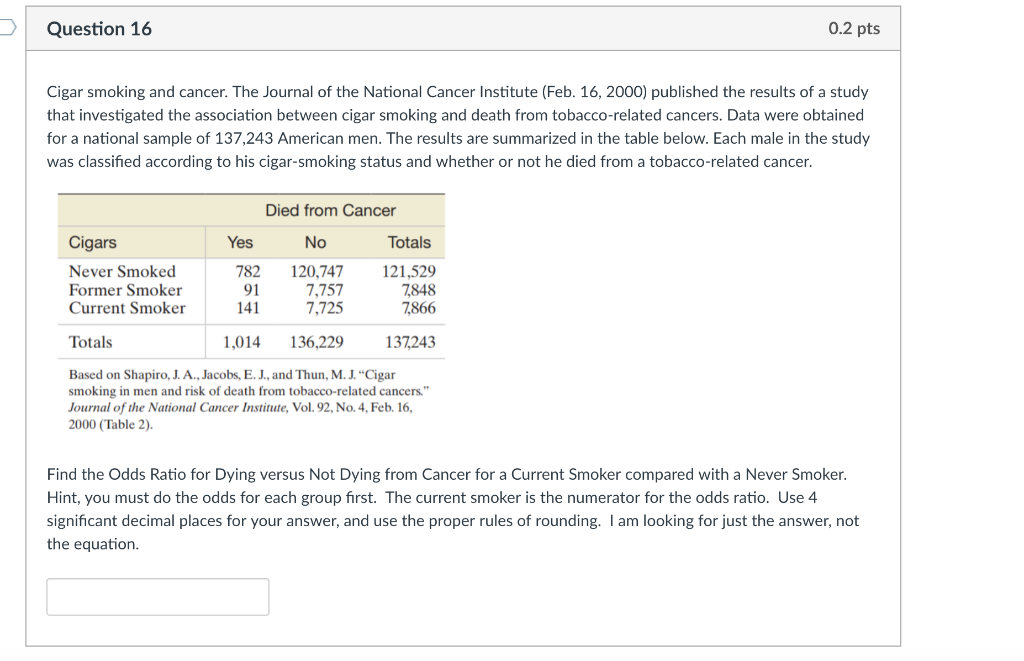
Solved Question 16 0 2 Pts Cigar Smoking And Cancer The Chegg Com

Odds Ratio Relative Risk

Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout
Summarising Binary Data Health Knowledge

The Behavior Of The Minimum Total Cost Versus Changing The Odds Ratio Download Scientific Diagram

Smoking And The Risk Of Microscopic Colitis A Meta Analysis

Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
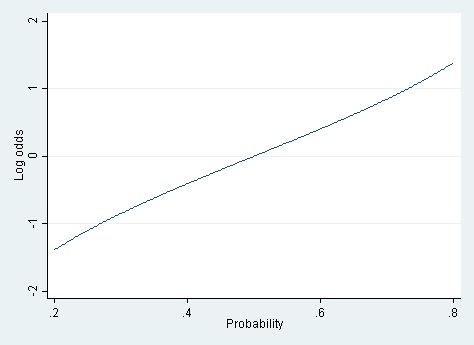
Linear Vs Logistic Probability Models Which Is Better And When Statistical Horizons

Ccyr Or Mmr Odds Ratios For Patients Receiving Bosutinib Versus Download Scientific Diagram

Table 2 From The Eœectiveness Of Commonly Used Lifting Assessment Methods To Identify Industrial Jobs Associated With Elevated Risk Of Low Back Disorders Semantic Scholar

Figure 4 Pre Operative Risk Assessment And Risk Reduction Before Surgery Jacc Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology
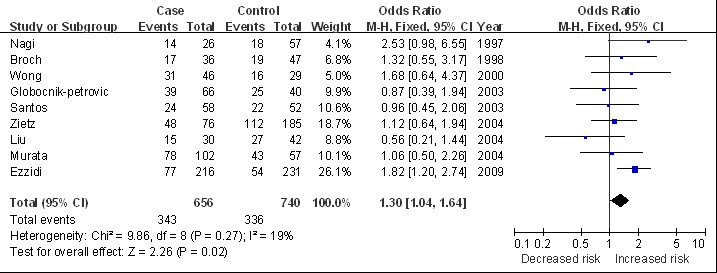
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 4g 5g Polymorphism And Retinopathy Risk In Type 2 Diabetes A Meta Analysis Bmc Medicine Full Text

Association Of Folate Pathway Gene Polymorphisms With The Risk Of Prostate Cancer A Population Based Nested Case Control Study Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prevention

Forest Plots Of Odds Ratio With 95 Ci For Apoe Polymorphism And Cra Download Scientific Diagram

Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To

Odds Ratio For The Risk Of Having A Prescription Pre Versus Download Table
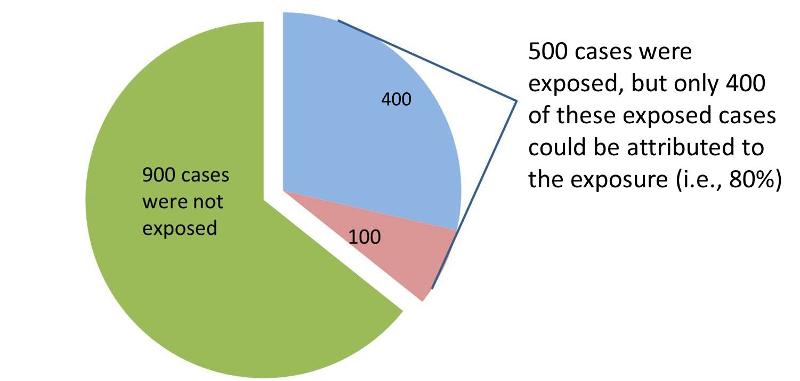
Measures Of Association
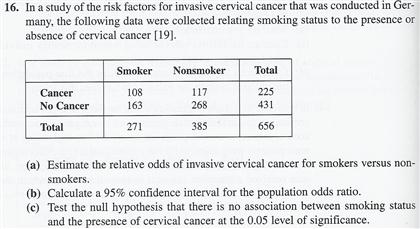
Solved In A Study Of The Risk Factors For Invasive Cervic Chegg Com
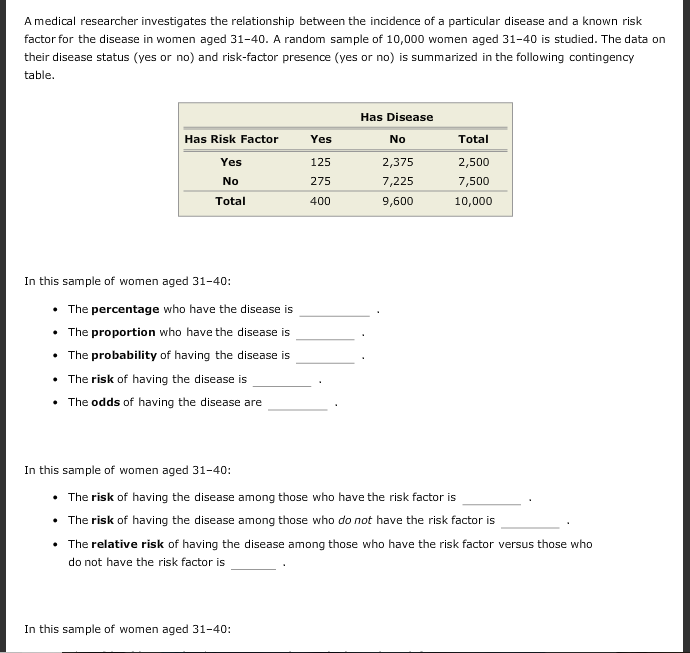
Based On This Chart The Top Of This Question Is P Chegg Com

Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download

Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1

Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs1tb C1nu Budoexfex5g5by5m1bbms6pp5jrpc30gseuerj99 Usqp Cau

Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood

Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download

Single Workplace Factor Odds Ratios Between High Risk Versus Low Risk Download Table
Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk
Solved Fig 5 Mr Scatter Plot Of Schizophrenia Risk Vs C Chegg Com

Single Workplace Factor Odds Ratios Between High Risk Versus Low Risk Download Table

Odds Ratio Article Statpearls

Table 3 From The Eœectiveness Of Commonly Used Lifting Assessment Methods To Identify Industrial Jobs Associated With Elevated Risk Of Low Back Disorders Semantic Scholar

Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk

The Odds Ratio For The Highest Versus The Lowest Selenium Exposure And Download Table

Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
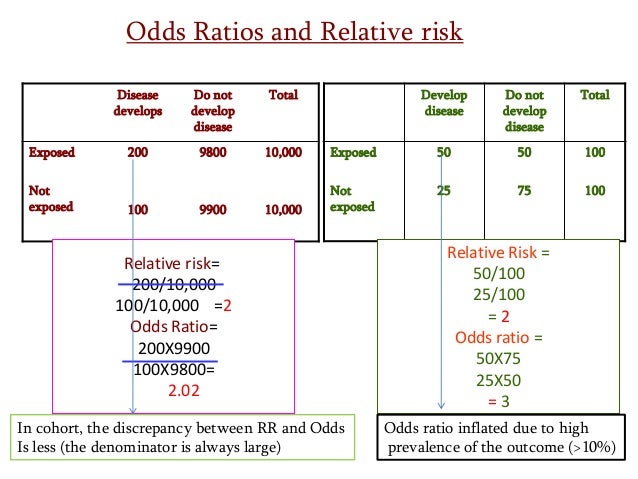
Estimating Risk

Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study Cohort Study Case Study Case Control Study

Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Abstract Europe Pmc

Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To

Odds Ratio Wikipedia
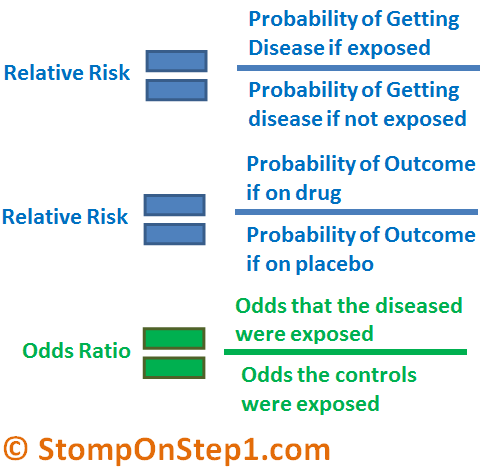
Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1

Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge

Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube

Ppt Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute Risk Differences And Risk Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id
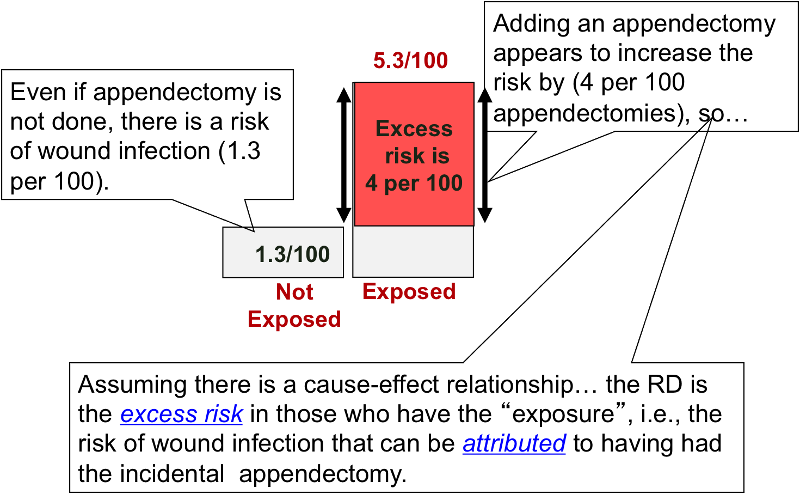
Risk Differences And Rate Differences
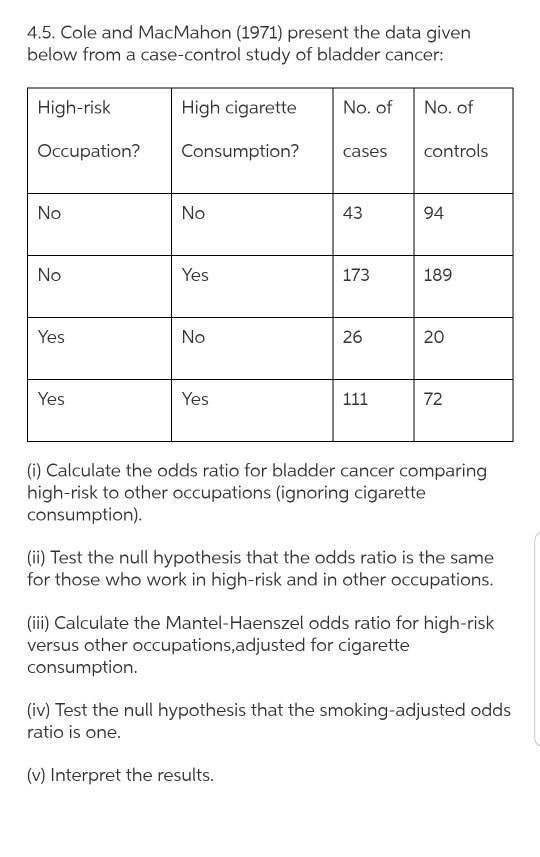
Solved 4 5 Cole And Macmahon 1971 Present The Data Giv Chegg Com

Forest Plot A Forest Plot Showing The Odds Ratio And Lower And Upper Download Scientific Diagram
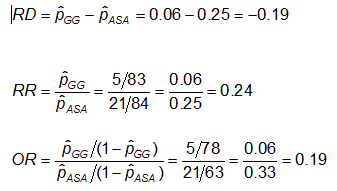
Cross Tabulation

Smoking And The Risk Of Microscopic Colitis A Meta Analysis
3

Solved In A Study Investigating Maternal Risk Factors For Chegg Com

Risk Of In Hospital Morbidity Mortality In Log Odds Versus Vitamin D Download Scientific Diagram

Sex Differences In Risk Factors For Myocardial Infarction Cohort Study Of Uk Biobank Participants The Bmj

Odds Ratio For Risk Factors Of Myocardial Infarction Worldwide In Old Download Scientific Diagram

Is It Safe For Me To Go To Work Risk Stratification For Workers During The Covid 19 Pandemic Nejm

Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine

Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
Plos One Is Gender Inequity A Risk Factor For Men Reporting Poorer Self Rated Health In The United States

Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club

Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj

How Much Normal Risk Does Covid Represent By David Spiegelhalter Wintoncentre Medium

View Image

How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube

A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence

What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
Session 5 Pih4009 N Risk

Stats Guidelines For Logistic Regression Models September 27 1999

Risk Classifications And Odds Of Fracture In Patients Classified As Download Table

Pooled Odds Ratio Or Of Risk Of Mortality In Vitamin D Deficient Download Scientific Diagram
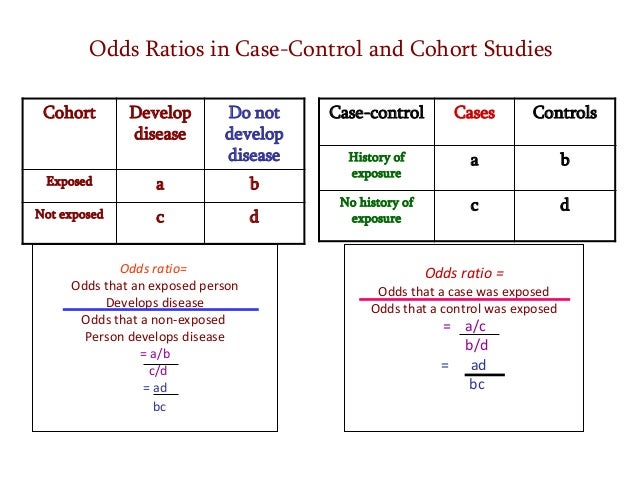
Estimating Risk

Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia
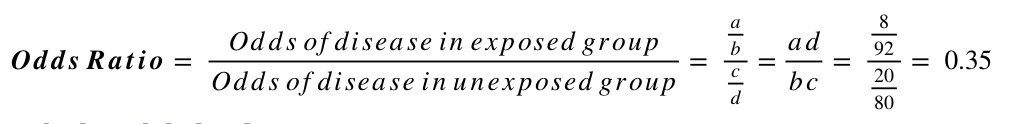
Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge

Table 1 From High Risk Human Papilloma Virus Hpv Infection Determined By Hybrid Capture Ii Assay In A Turkish University Hospital Outpatient Clinic Semantic Scholar
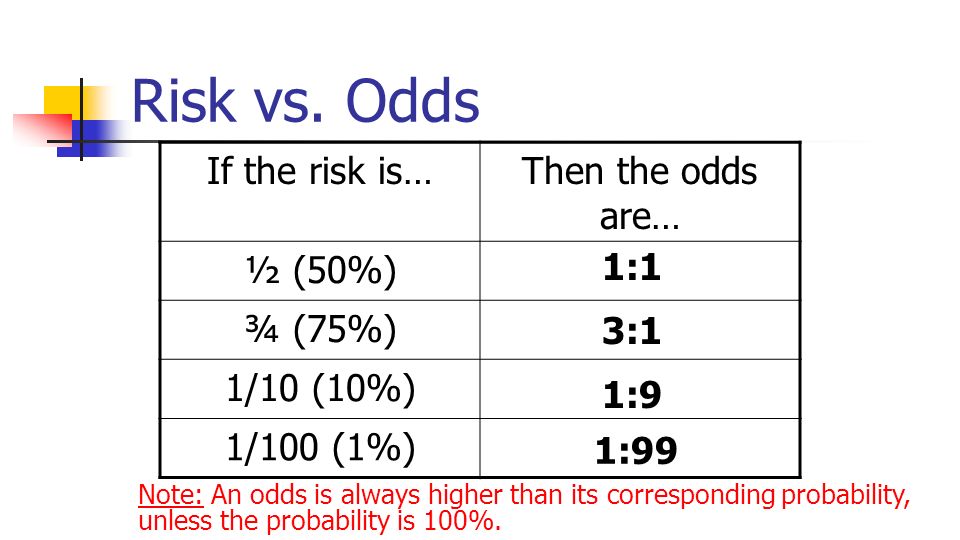
Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download
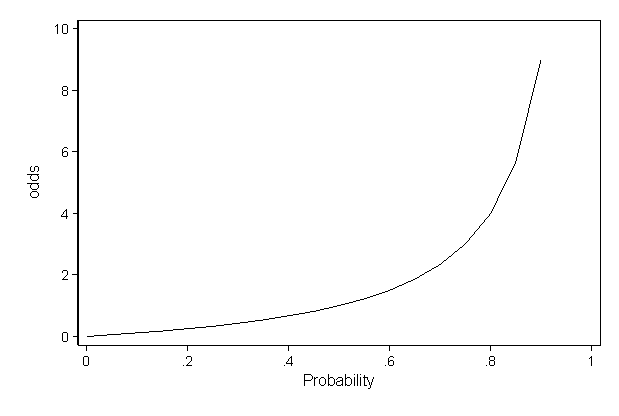
Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression

Association Of Folate Pathway Gene Polymorphisms With The Risk Of Prostate Cancer A Population Based Nested Case Control Study Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prevention
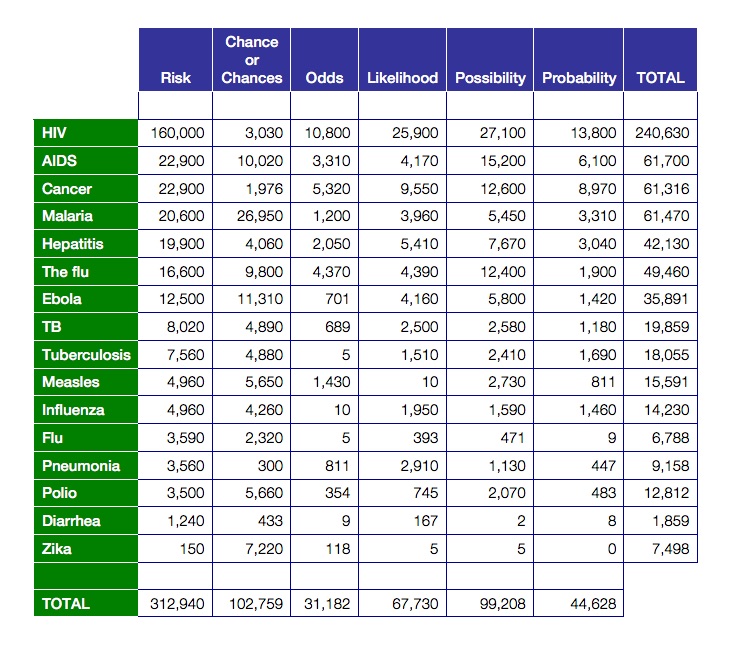
Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications
2
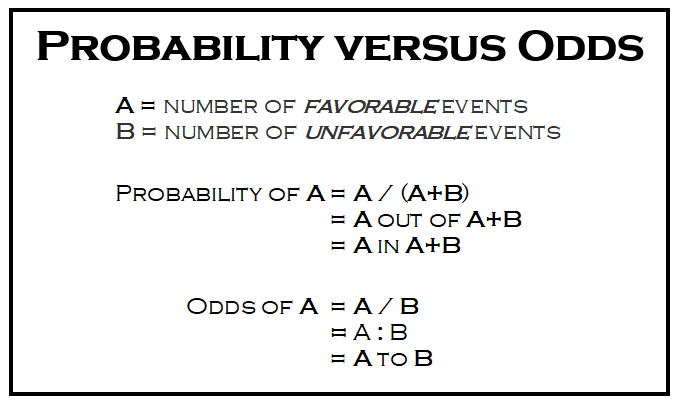
What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog

Or2rr
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsg4su2mr8na0fhj Fifitqg198udx Emcfjr4lbf73sjgn9d K Usqp Cau

Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table

Figure 1 Risk Of Premature Atherosclerotic Disease In Patients With Monogenic Versus Polygenic Familial Hypercholesterolemia Jacc Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology
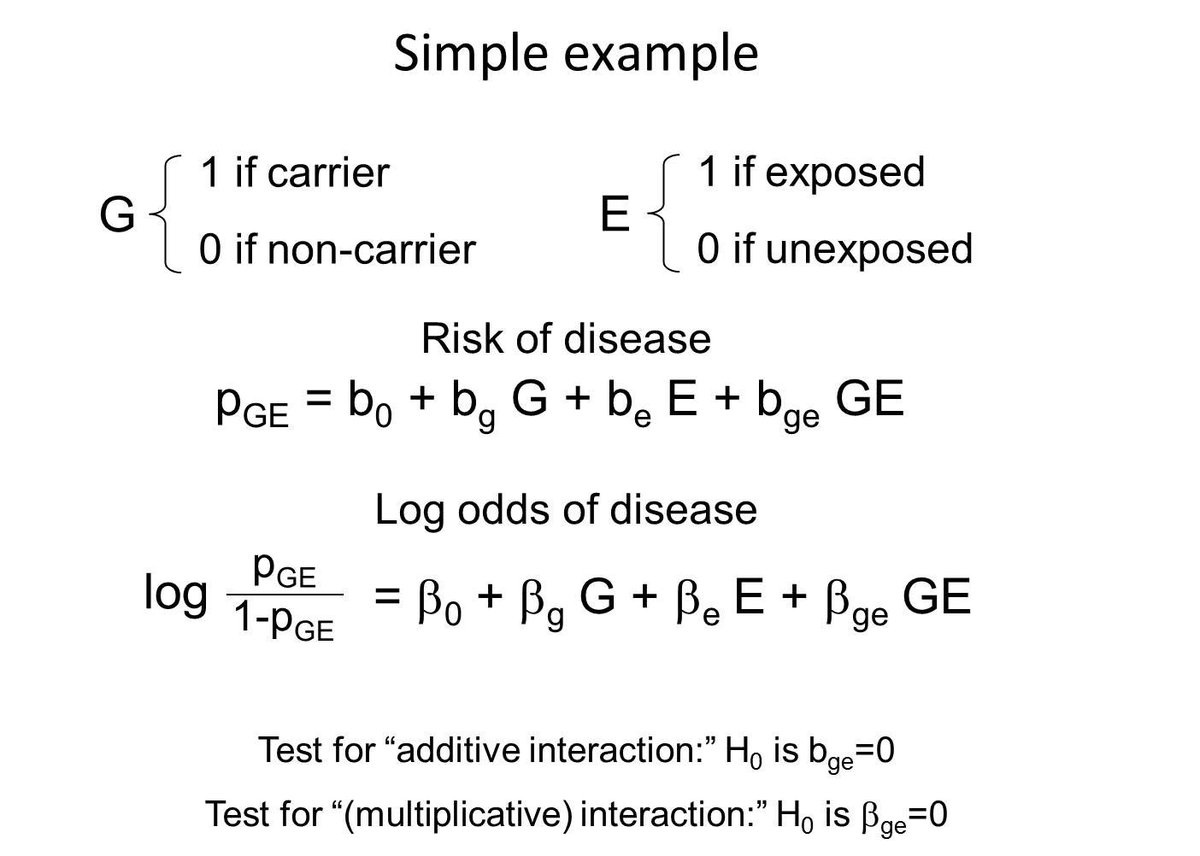
Pete Kraft If The Odds Ratio Comparing Exposed To Non Exposed Individuals Differs By Genotype I E Betage 0 Then We Typically Call That A Multiplicative Interaction Or More Verbosely Departures

Lecture3

Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram
The Math Behind Betting Odds Gambling
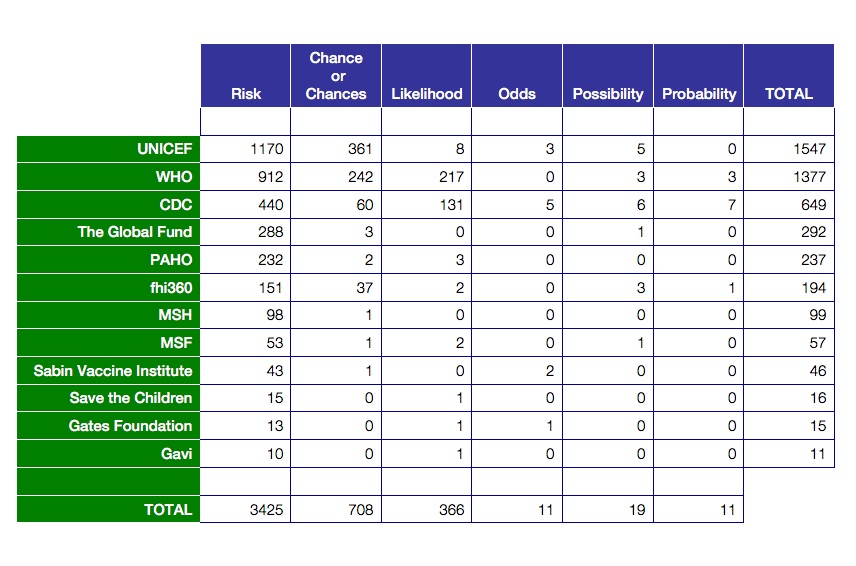
Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications

Estimating Risk

Odds Ratios Of Cardiovascular Risks In Intervention Versus Control Download Table

Figure 1 Model Predicted Odds Ratios Comparing Extirpation Risk Across Island Conditions

A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
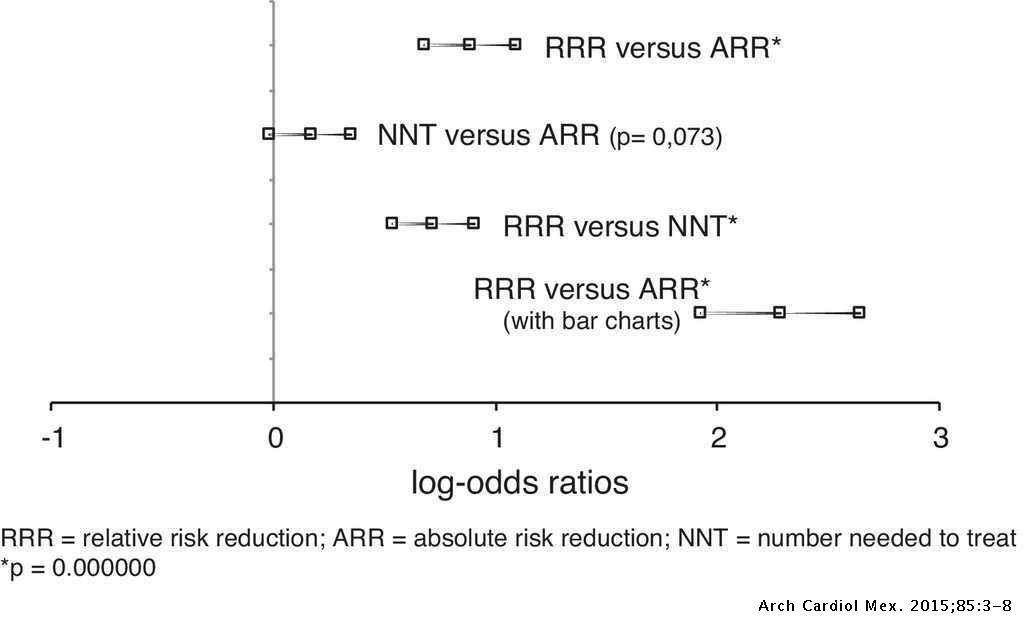
Effects Of Presenting Risk Information In Different Formats To Cardiologists A Latin American Survey Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico

The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor

Relative Risk Wikipedia

Odds Ratio Wikipedia
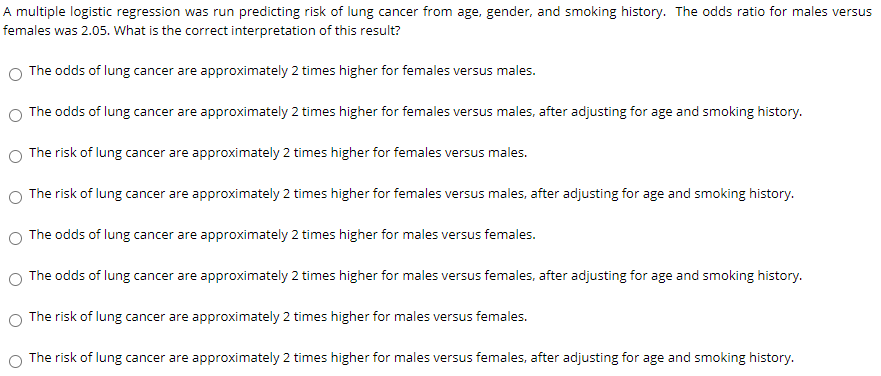
Solved A Multiple Logistic Regression Was Run Predicting Chegg Com

Observational Studies The Ebm Project

Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



